HVAC Meaning: What Is HVAC And What Does HVAC Stand For?
By Travis Baugh
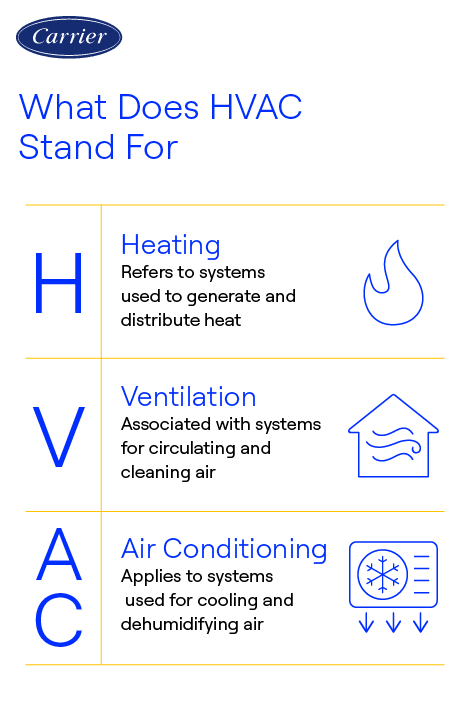
HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. Whether it's about heating your living space during chilly winter months or cooling it down on scorching summer days, HVAC systems are fundamental to ensuring a pleasant temperature and clean air. But what is HVAC how exactly does HVAC work? Let's dive into the meaning of HVAC and discover how it keeps your home cozy and comfortable throughout the year.
What is HVAC and What Does HVAC Stand For?
Components of an HVAC System
- Heating: This part of the system is responsible for warming the indoor air during colder months, typically using furnaces , boilers , or heat pumps .
- Ventilation: Ventilation involves the exchange of indoor and outdoor air, which helps to maintain indoor air quality by removing contaminants, odors, and excess moisture, and introducing fresh air.
- Air Conditioning: This component cools the indoor air during warmer months, usually through the use of air conditioners or heat pumps.
- Thermostat: A thermostat inside the home controls the entire HVAC system. You can set your desired temperature, and the system will automatically switch between heating, cooling, or just circulating air as needed.
- Ductwork: Ductwork distributes air throughout the home
- Vents or registers: Vents and registers are used for air circulation.
- Indoor air quality products: Additionally, air purifiers, humidifiers, and dehumidifiers and other indoor air quality products may be integrated into the system to further enhance comfort and air quality.
How Does HVAC Work?

Types of HVAC Products
Air Conditioners
Heat Pumps
Furnaces
Boilers
Fan Coils
Evaporator Coils
An evaporator coil is a key component of an HVAC system that absorbs heat from indoor air as refrigerant passes through it, enabling the cooling process in air conditioners and heat pumps.Ductless Mini-Splits
Thermostats
Ventilation Systems
Humidifiers & Dehumidifiers
Air Purifiers

What HVAC System is Right for Me?
- The size and age of your home can affect how much heating or cooling power you need.
- Your home’s design and layout, including ceiling height and window placement, can impact airflow and temperature balance.
- The local climate plays a big role in determining whether you need a stronger focus on heating, cooling, or both.
- The condition of your existing ductwork (if any) may influence whether a ducted or ductless system is the better fit.

Frequently Asked Questions About HVAC Meaning
Find an HVAC Dealer Near Me
At Carrier, we offer a wide range of HVAC solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of your home. Our HVAC systems are designed to deliver comfort, energy efficiency, and reliability. Whether you are looking for new HVAC system installation or need expert maintenance and repair services, contact your local Carrier dealer to achieve a comfortable and healthy home environment. By understanding the HVAC meaning and HVAC definition, you can make the best choices for your home's needs.



