What Is a Heat Pump And How Does A Heat Pump Work?
By Travis Baugh
So, what is a heat pump and how does a heat pump work? A heat pump is part of a home heating and cooling system and is installed outside your home. Like an air conditioner such as central air, it can cool your home, but it’s also capable of providing heat. In cooler months, a heat pump pulls heat from the cold outdoor air and transfers it indoors, and in warmer months, it pulls heat out of indoor air to cool your home. They are powered by electricity and transfer heat using refrigerant to provide comfort all year round. Because they are able to both heat and cool a residence, homeowners may not need to install separate systems to heat their homes. In colder climates, an electric heat strip can be added to the indoor fan coil for additional capabilities. Heat pumps do not burn fossil fuels like furnaces do, making them more environmentally friendly.
What Types of Heat Pumps Are There?
The two most common types of heat pumps are air-source and ground-source. Air-source heat pumps transfer heat between indoor air and outdoor air, and are more popular for residential heating and cooling.
Ground-source heat pumps, sometimes called geothermal heat pumps, transfer heat between the air inside your home and the ground outside. These are more expensive to install but are typically more efficient and have a lower operating cost due to the consistency of the ground temperature throughout the year.
HOW DOES A HEAT PUMP WORK?
How does a heat pump work? Heat pumps transfer heat from one place to another by different air or heat sources. Air source heat pumps move heat between the air inside a home and the air outside a home, while ground source heat pumps (known as geothermal heat pumps) transfer heat between the air inside a home and the ground outside a home. We will focus on air source heat pumps, but the basic operation is the same for both.

HEAT PUMP BASICS
Despite the name, heat pumps do not generate heat – they move heat from one place to another. A furnace creates heat that is distributed throughout a home, but a heat pump absorbs heat energy from the outside air (even in cold temperatures) and transfers it to the indoor air. When in cooling mode a heat pump and an air conditioner are functionally identical, absorbing heat from the indoor air and releasing it through the outdoor unit. Click here for more information about heat pumps vs air conditioners.
When considering which type of system is best for your home, several important factors should be considered, including the size of the home and the local climate. A local Carrier dealer has the expertise to properly explain heat pumps, evaluate your specific needs and help you make the right decision.
Where Do Heat Pump Systems Work Best?
Homeowners in need of a new heating or cooling system, may consider the type of climate they live in before purchasing a heat pump system. Heat pumps are more common in milder climates, where the temperature does not typically drop below freezing. In colder regions, they can also be combined with furnaces for energy-efficient home heating on all but the coldest days. When the temperature outside drops too low for the heat pump to operate effectively, the system will instead use the furnace to generate heat. This kind of system is often called a dual fuel system – it is very energy efficient and cost effective.
IMPORTANT COMPONENTS OF A HEAT PUMP SYSTEM
A typical air source heat pump system consists of two major components, an outdoor unit (which looks just like the outdoor unit of a split-system air conditioning system) and an indoor air handler unit. Both the indoor and outdoor unit contain various important sub-components.
OUTDOOR UNIT
The outdoor unit contains a coil and a fan. The coil operates as either a condenser (in cooling mode) or an evaporator (in heating mode). The fan blows outside air over the coil to facilitate the heat exchange.
INDOOR UNIT
Like the outdoor unit, the indoor unit, commonly referred to as the air handler unit, contains a coil and a fan. The coil acts as an evaporator (in cooling mode) or a condenser (in heating mode). The fan is responsible for moving air across the coil and throughout the ducts in the home.
REFRIGERANT
The refrigerant is the substance that absorbs and rejects heat as it circulates throughout the heat pump system.
COMPRESSOR
The compressor pressurizes the refrigerant and moves it throughout the system.
REVERSING VALVE
The part of the heat pump system that reverses the flow of refrigerant, allowing the system to operate in the opposite direction and switch between heating and cooling.
EXPANSION VALVE
The expansion valve acts as a metering device, regulating the flow of the refrigerant as it passes through the system, allowing for a reduction of pressure and temperature of the refrigerant.
HOW DOES A HEAT PUMP COOL AND HEAT?
Heat pumps do not create heat. They redistribute heat from the air or ground and use a refrigerant that circulates between the indoor fan coil (air handler) unit and the outdoor compressor to transfer the heat.
In cooling mode, a heat pump absorbs heat inside your home and releases it outdoors. In heating mode, the heat pump absorbs heat from the ground or outside air (even cold air) and releases it indoors.
HOW DO HEAT PUMPS WORK - COOLING MODE
One of the most important things to understand about heat pump operation and the process of transferring heat is that heat energy naturally wants to move to areas with lower temperatures and less pressure. Heat pumps rely on this physical property, putting heat in contact with cooler, lower pressure environments so that the heat can naturally transfer. This is how a heat pump works.
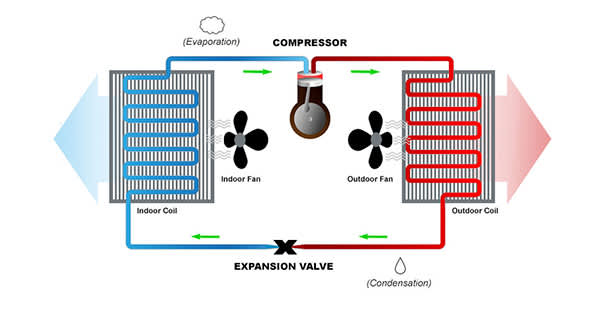
STEP 1
Liquid refrigerant is pumped through an expansion device at the indoor coil, which is functioning as the evaporator. Air from inside the house is blown across the coils, where heat energy is absorbed by the refrigerant. The resulting cool air is blown throughout the home’s ducts. The process of absorbing the heat energy has caused the liquid refrigerant to heat up and evaporate into gas form.
STEP 2
The gaseous refrigerant now passes through a compressor, which pressurizes the gas. The process of pressurizing the gas causes it to heat up (a physical property of compressed gases). The hot, pressurized refrigerant moves through the system to the coil in the outdoor unit.
STEP 3
A fan in the outdoor unit moves outside air across the coils, which are serving as condenser coils in cooling mode. Because the air outside the home is cooler than the hot compressed gas refrigerant in the coil, heat is transferred from the refrigerant to the outside air. During this process, the refrigerant condenses back to a liquid state as it cools. The warm liquid refrigerant is pumped through the system to the expansion valve at the indoor units.
STEP 4
The expansion valve reduces the pressure of the warm liquid refrigerant, which cools it significantly. At this point, the refrigerant is in a cool, liquid state and ready to be pumped back to the evaporator coil in the indoor unit to begin the cycle again.
HOW DOES A HEAT PUMP WORK - HEATING MODE
A heat pump in heating mode operates just like cooling mode, except that the flow of refrigerant is reversed by the aptly named reversing valve. The flow reversal means that the heating source becomes the outside air (even when outdoor temperatures are low) and the heat energy is released inside the home. The outside coil now has the function of an evaporator, and the indoor coil now has the role of the condenser.
The physics of the process are the same of how a heat pump works in cooling mode. Heat energy is absorbed in the outdoor unit by cool liquid refrigerant, turning it into cold gas. Pressure is then applied to the cold gas, turning it to hot gas. The hot gas is cooled in the indoor unit by passing air, heating the air and condensing the gas to warm liquid. The warm liquid is relieved of pressure as it enters the outdoor unit, turning it to cool liquid and renewing the cycle.
Air Source Heat Pump

HOW DO HEAT PUMP WORKS – REVIEW
Electric heat pumps are versatile, efficient cooling and heating systems. Thanks to a reversing valve, a heat pump can change the flow of refrigerant and either heat or cool a home. Air is blown over an evaporator coil, transferring heat energy from the air to the refrigerant. That heat energy is circulated in the refrigerant to a condenser coil, where it is released as a fan blows air across the coil. Through this process, heat is pumped from one place to another.
Now that we have explained how does a heat pump work, a local Carrier HVAC expert can help evaluate your home's heating and cooling requirements and recommend the proper HVAC system for your home. Your Carrier dealer can further explain heat pumps and help you make the best decision for you and your family's comfort.
HOW DO HEAT PUMPS WORK FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Explore Carrier Heat Pumps
Choosing a Carrier heat pump offers reliable performance and energy efficiency, making it an excellent long-term investment for both heating and cooling needs. With advanced technology and a strong reputation for durability, Carrier heat pumps provide optimal comfort while helping to lower heating and cooling bills. Our commitment to sustainability and quiet operation can help enhance your overall home environment. Explore Carrier's line of heat pumps today.
Our highest efficiency and most advanced air conditioner with up to 23 SEER2 for premium energy savings with extremely quiet performance and premium comfort features.
Up to 18 SEER2 for enhanced energy savings with enhanced comfort features. Features InteliSense™ technology
Up to 16 SEER2 for moderate energy savings with standard comfort features.
- Learn about the differences of a heat pump vs air conditioning.
- What is a heat pump vs furnace?
- Get information about the Cost of a Heat Pump
- Learn about Heat Pump Efficiency and SEER Ratings
- Learn about Heat Pump Troubleshooting
- Heat Pump Not Heating Or Cooling
- Heat Pump Service
- Heat Pumps: A Sustainable Comfort Solution
- What is an HVAC Split System and What is Split Air Conditioning?
- Types of Heating and Cooling Systems Explained
- Discover heat pump tax credits
- In need of heat pump repair?
- Learn about heat pump installation
- How much will a heat pump increase my electric bill?
- Get in the know on cold climate heat pumps
- HVAC meaning: What is HVAC?
- Learn if you need a 3 ton heat pump
- What is a two-stage HVAC system?
- Discover what an air source heat pump is




