Understanding Heat Exchangers
A heat exchanger is an integral part of heating and cooling systems, facilitating the efficient transfer of heat from one medium to another. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various types of heat exchangers, how heat exchangers work, applications, and the importance of heat exchanger.
What is a heat exchanger?
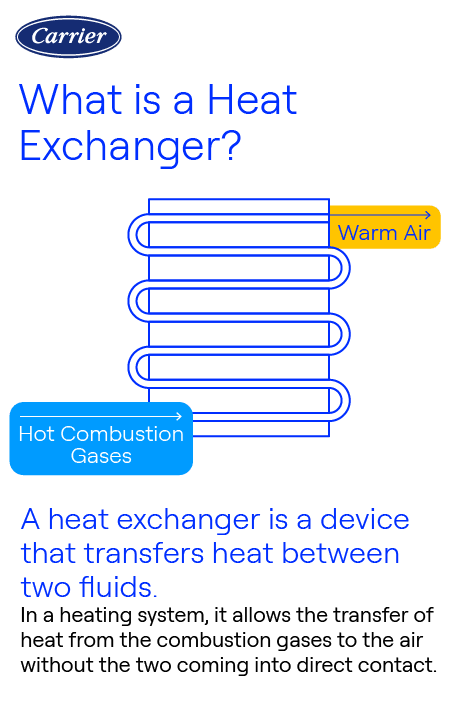
A heat exchanger is a fundamental component within heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, responsible for transferring heat between the air streams in order to regulate indoor temperatures. It plays a critical role in both heating and cooling processes, allowing for efficient energy usage and comfortable indoor environments. Understanding the function, types, and maintenance of HVAC heat exchangers is essential for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of HVAC systems.
How Heat Exchangers Work
Heat exchangers are essential in HVAC systems, transferring heat between air and liquid, or between two different liquid circuits, to regulate indoor temperature efficiently. Understanding the principles of heat transfer, liquid flow, and heat exchanger efficiency can help homeowners make informed decisions about their heating and cooling systems.
- Principles of Heat Transfer: Heat transfer occurs through conduction, convection, and radiation. In heat exchangers, conduction involves heat transfer through direct contact between solids, convection through fluid movement (either forced or natural), and radiation through electromagnetic waves.
- Fluid Flow and Heat Exchange: Heat exchangers transfer heat between two fluids, often called the hot fluid and the cold fluid. The hot fluid transfers its heat to the cold fluid through tubes or plates within the exchanger, ensuring maximum surface area contact for efficient heat transfer.
- Heat Exchanger Efficiency: Efficiency depends on the exchanger's ability to transfer heat effectively while minimizing energy losses. Factors affecting efficiency include design, size, material, fluid flow rates, and temperature differences. Higher efficiency heat exchangers provide better performance and lower energy consumption, reducing operating costs for homeowners.
Applications of HVAC Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are crucial in various applications, including heating and cooling systems . Whether maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature or regulating industrial processes, heat exchangers ensure efficient heat transfer.
In heating systems, heat exchangers transfer heat from a source (like a furnace or boiler ) to the air or water circulating throughout a home, ensuring even distribution of warmth during cold weather. Designed to maximize heat transfer while minimizing energy consumption, boiler or furnace heat exchangers are key components of energy-efficient heating systems.
Importance of HVAC Heat Exchangers
| Role | Why It Matters |
| Energy Efficiency | HVAC heat exchangers play a crucial role in maximizing energy efficiency by facilitating the transfer of thermal energy between air streams. This allows HVAC systems to maintain desired indoor temperatures while minimizing energy consumption. |
| Comfort | By regulating indoor temperatures effectively, HVAC heat exchangers contribute to occupant comfort and well-being. They ensure consistent and comfortable indoor environments year-round. |
| System Performance | Properly functioning heat exchangers are essential for the overall performance and reliability of HVAC systems. They help prevent issues such as overheating, insufficient heating or cooling, and energy waste. |
| Longevity | Regular maintenance and proper care of HVAC heat exchangers by a Carrier professional can extend the lifespan of the entire HVAC system. This includes cleaning, inspection, and timely repairs to address any issues that may arise. |
Kevin Dickson, president of Energy Services Air Conditioning, Heating and Electrical in Naperville, Illinois, says the heat exchanger is a vital part of the furnace’s performance.
“The heat exchanger is the heart of the furnace,” Dickson said. “A failed heat exchanger can lead to the need to repair or replace your furnace prematurely. Assuring your furnace is properly sized and installed can help protect your heat exchanger and furnace’s lifespan.”
Heat Exchanger Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance is essential for optimal performance and longevity of heat exchangers. Following recommended cleaning and maintenance procedures, troubleshooting common issues, and taking steps to prolong the heat exchanger's lifespan can ensure efficient heating in your home for years.
Cleaning and Maintenance Procedures
Regular cleaning prevents dirt, debris, and mineral deposits from hindering efficiency.
- Turn off the heating system and let it cool.
- Remove the access panel to reach the heat exchanger.
- Use a soft brush or vacuum to clear loose debris.
- For stubborn deposits, use a mild detergent solution, then rinse thoroughly.
- Let the heat exchanger dry completely before reassembling.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues include cracked or damaged heat exchangers, which can cause carbon monoxide leaks and pose safety risks. Signs of a damaged heat exchanger include:
- Soot accumulation
- Unusual odors
- A yellow flame instead of blue.
Contact a qualified HVAC contractor immediately if you notice these signs. Other issues include:
- Airflow restrictions
- Improper fuel combustion
- Thermostat malfunctions
Regular inspections and maintenance can identify and resolve these problems early. Schedule regular air conditioner maintenance and furnace service with your local Carrier dealer to extend the lifespan of your HVAC system and heat exchanger. A trained technician can detect and address issues early, preventing costly repairs or replacements. Ensure proper airflow by cleaning or replacing air filters regularly to prevent overheating and strain on the heat exchanger. Learn more about how to change air conditioner filters and how often to replace the air filter .
Three Types of HVAC Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are pivotal in heating and cooling systems, enabling the transfer of heat between fluids. Different types of heat exchangers serve various applications, each offering unique designs and functionalities. Understanding these types can help you make an informed choice. Here are three popular types of heat exchangers:
Plate and Frame Heat Exchangers
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
Contact A Carrier Dealer To Choose The Right Heat Exchanger
Contacting your local Carrier dealer ensures you select the right heat exchanger for your HVAC system. Their expert guidance will help you choose a unit that matches your system’s capacity, efficiency needs, and environmental considerations. With their professional recommendations, you can optimize performance and enhance energy savings.
Regular maintenance and proper care by your local Carrier dealer are key to ensuring the longevity and reliability of HVAC heat exchangers, thereby prolonging the lifespan of HVAC systems and helping reduce operating costs.



