About The Author: Travis Baugh is a Digital Brand Marketing Manager for Carrier, where he develops informative, straightforward content to help homeowners better understand heating, cooling, and indoor air quality. His writing is focused on empowering homeowners to make confident, well-informed choices about their home comfort systems.
HVAC Education, Furnaces
Furnace Ignitor: Understanding its Function and Importance
The furnace ignitor is a critical component in the heating system of your home. Understanding the operation of a furnace ignitor can help you identify and troubleshoot potential furnace issues. This article will explore the workings of a furnace ignitor, signs of a faulty ignitor, and essential tips for maintaining and troubleshooting this vital part of your heating system.
How Does a Furnace Ignitor Work?
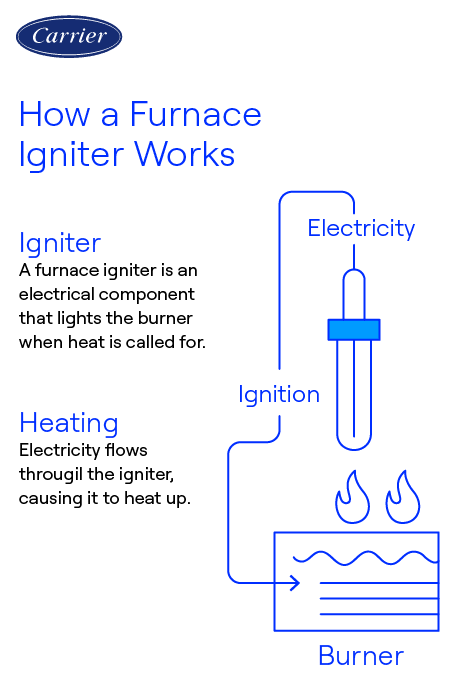
The furnace ignitor is essential for initiating the heating process in your furnace. It ignites the fuel, such as gas or oil, to produce the heat required to warm your home. Without a functioning ignitor, your furnace would be unable to start and provide the necessary warmth.
There are various types of furnace ignitors, each serving a specific function. The most common types include hot surface ignitors, spark ignitors, and intermittent pilot ignitors.
- Hot surface ignitors are the most widely used type. They consist of a heating element made from materials like silicon carbide or silicon nitride. When electrical current flows through the ignitor, the heating element heats up and emits a bright glow. This glow then ignites the fuel, starting the combustion process.
- Spark ignitors use an electric spark to ignite the fuel. They typically consist of an electrode and a spark gap. When electrical current is applied, a spark is generated between the electrode and the gap, igniting the fuel.
- Intermittent pilot ignitors are commonly found in newer furnace models. These ignitors use a small pilot flame that is ignited by an electronic spark. The pilot flame then ignites the main burner, initiating the heating process.
Furnace ignitors are made from various materials, depending on the type and model. Silicon carbide is a popular choice due to its durability and resistance to high temperatures. Silicon nitride is another commonly used material known for its excellent thermal conductivity and reliability.
Now that you understand how a furnace ignitor works, it's important to ensure your ignitor is properly maintained and functioning. Regular inspection and cleaning can prevent issues and ensure your gas furnace ignitor operates efficiently throughout the colder months.
How to Identify a Faulty Furnace Ignitor
If your furnace is not working properly, a faulty ignitor could be the culprit. The ignitor is a critical component that initiates the combustion process. Over time, it may wear out or malfunction, leading to various problems. By learning how to identify a faulty furnace ignitor, you can take the necessary steps to resolve the issue and restore your heating system's functionality.
Several warning signs indicate a failing furnace ignitor:
- The most common sign is a furnace that fails to ignite or takes a long time to heat up. If you notice your furnace repeatedly attempting to start without success, a faulty ignitor is likely to blame.
- Additionally, a dim or no glow coming from the ignitor is another indicator of a problem. Some furnaces may also display error codes or flashing lights to alert you to an ignitor issue.
A malfunctioning furnace ignitor can be caused by various factors:
- One common cause is normal wear and tear over time. Ignitors are subjected to extreme temperatures and can weaken or crack with extended use.
- Excessive voltage fluctuations or power surges can also damage the ignitor.
- Additionally, the presence of dirt, dust, or debris on the ignitor can interfere with its proper functioning.

Furnace Ignitor Maintenance
Scheduling regular furnace maintenance with your local Carrier dealer typically includes the maintenance and cleaning of your furnace ignitor to ensure its proper functioning. The following steps are typically followed:
- Power is turned off: The power supply is turned off to the furnace to prevent any accidents or injuries.
- Ignitor is cleaned: Dirt or debris are gently removed from the ignitor using a soft brush or cloth. Abrasive materials that may damage the ignitor.
- Inspection for wear and tear: The ignitor is checked for any signs of wear and tear, such as cracks or corrosion. If damage is noticed, it's best to replace the ignitor to prevent potential issues.

Furnace Ignitor Troubleshooting
When it comes to identifying issues with your gas furnace ignitor, proper inspection techniques are essential. Your local Carrier dealer will perform these steps to ensure a thorough inspection:
- Visual inspection: The HVAC contractor will carefully examine the ignitor for any visible damage or abnormalities, looking for cracks, discoloration, or loose connections.
- Test the ignitor: The HVAC contractor will use a multimeter to test the ignitor's resistance. If the reading is significantly different from the manufacturer's specifications, it may indicate a faulty ignitor.
- Consult the user manual: The furnace's user manual will have specific troubleshooting steps and diagnostic codes related to the ignitor. This will help you identify and address any issues effectively.
- Replace the ignitor: If cleaning and inspection don't resolve the issue, it may be necessary to replace the ignitor. Make sure to purchase a compatible ignitor from a reputable source for your furnace ignitor replacement needs.
Learn more about furnace troubleshooting in our comprehensive guide.
Connect With Your Carrier Dealer For Your Furnace Ignitor Needs
Remember, regular maintenance and timely troubleshooting can help you avoid costly repairs and ensure your furnace ignitor operates smoothly. If you need further assistance or encounter complex problems, it's best to consult your local Carrier dealer for a furnace ignitor replacement.

Frequently Asked Questions About Furnace Ignitors
It is best to let an HVAC professional reset a furnace ignitor. First, they will turn off the furnace power and gas. They will wait 5-10 minutes for safety, then turn the power back on. If the ignitor still doesn’t work, they will check for issues like dirt or wear.
A furnace ignitor typically costs between $20 to $150, depending on the brand and model of your furnace. Labor costs for professional installation can add an additional $100 to $300. Prices vary based on the complexity of the repair and your location.
A furnace ignitor can fail due to wear and tear from repeated heating cycles, dirt buildup, electrical issues, or corrosion. A faulty igniter may also result from a power surge or temperature fluctuations, preventing it from properly igniting the gas.
Signs of a bad furnace ignitor include no flame or heat, clicking sounds without ignition, or a furnace not starting. You might also notice a steady blinking light on the control board, indicating an ignition failure. An HVAC professional should inspect and replace the ignitor if needed.
While it’s possible to replace your own furnace ignitor, it’s best to leave it to an HVAC professional. Working with gas and electrical components can be dangerous without proper knowledge and tools. An HVAC technician can ensure the job is done safely and correctly.

