HVAC System and HVAC Unit
Whether you're a homeowner seeking an upgrade for your current HVAC system or simply interested in the different types of HVAC units, this article will provide you with essential insights. Additionally, we will guide you on how to choose the right HVAC system for your home, along with tips on installation and maintenance. Let’s begin our exploration of HVAC systems!

What is an HVAC System?
An HVAC system, standing for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning, is vital for maintaining comfort and optimal indoor air quality in your home. An HVAC system regulates temperature, humidity, and air circulation within a home, consisting of interconnected components working in unison to achieve the desired indoor climate. The core components of an HVAC system include
- Heating: This component provides warmth during colder months through various methods like furnaces, boilers, or heat pumps.
- Ventilation: Ventilation systems expel stale air and introduce fresh outdoor air, filtering out pollutants, allergens, and odors to enhance indoor air quality.
- Air Conditioning: This component cools the indoor environment during warm weather, ensuring a comfortable temperature.
HVAC systems provide thermal comfort, allowing homeowners to maintain a consistent indoor temperature year-round, which is especially crucial during extreme weather conditions. Secondly, they help regulate humidity levels, balancing excess moisture that could lead low humidity that may cause dryness and discomfort. Lastly, HVAC systems help improve indoor air quality by filtering out pollutants, allergens, and contaminants to promote overall well-being.
Types of HVAC Systems
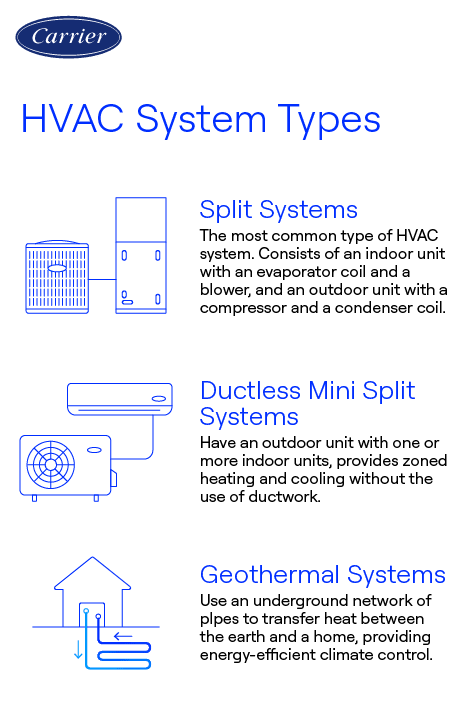
HVAC systems (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) come in several types, each designed to provide optimal climate control in your home. Here’s an overview of the most common types.Split Systems
A split HVAC system is a heating system or air conditioning system that has indoor and outdoor units connected to each other with copper tubing. The outdoor portion of the system typically contains the condenser and compressor, while the indoor portion of the system has an evaporator coil and indoor air handling unit that sends the air through the ductwork in your home Learn more about what is a split system.
Ductless Mini Split Systems
Ductless mini split systems do not require ductwork and consist of an outdoor condenser unit connected to one or more indoor units. Ductless mini-split systems provide zoned heating and cooling, allowing independent temperature control in different areas of your home. Ductless mini split systems are ideal for retrofitting older homes or adding climate control to individual rooms. Packaged HVAC Systems In packaged systems, all components (compressor, condenser, and evaporator) are housed in a single unit outside of the home. These units are typically installed at homes with limited indoor space for separate units. Packaged products can be powered three different ways. Cooling-only packaged products run exclusively on electricity, gas heating and cooling units use gas for heating and electricity for cooling., while heat pump packaged products use electricity to both heat and cool. Learn more about what is a ductless mini split.
Geothermal HVAC Systems
Geothermal HVAC equipment use the earth’s stable underground temperature to heat and cool homes. Pipes are buried underground, circulating fluid that absorbs or dissipates heat. Geothermal heat pumps provide energy-efficient performance to give you comfortable indoor comfort within your home. Geothermal HVAC systems come in four different loop types (horizontal, vertical, pond, and open loop) which all work differently to extract water to heat and cool your home. Learn more about what is geothermal heating.

Types of HVAC Units
HVAC equipment refers to the various devices and components used to manage heating, cooling, ventilation, and air quality in a building. Here's a breakdown of the common types of HVAC units.
Heat Pumps
A heat pump transfers heat between indoors and outdoors to provide both heating and cooling. In heating mode, it extracts heat from the outside air (or the ground for a geothermal heat pump) and moves it inside, while in cooling mode, it reverses the process, removing heat from inside and releasing it outdoors. Heat pumps are versatile and work well in moderate climates for year-round comfort.
Air Conditioners
An air conditioner cools indoor spaces by extracting heat and moisture from the air. It works by circulating refrigerant through a system of coils, where warm air is absorbed, cooled, and then blown back into the room, while the extracted heat is expelled outside. This process creates a comfortable indoor environment by reducing temperature and humidity.
Furnaces
A furnace heats air and distributes it through a home via ductwork. Furnaces have three different fuel types: natural gas, oil, and electricity. Modulating furnaces can adjust heat output in small increments for maximum efficiency, two-stage furnaces can operate at two different speeds (low and high), improving efficiency and comfort. Single-stage furnaces operate at full capacity or are off.
Fan Coils
A fan coil moves air inside your home by blowing air over a coil containing hot or cold water. It works by circulating air through the coil, where the air absorbs heat or releases it, depending on whether heating or cooling is needed. Fan coils are a complement to your air conditioner or heat pump.
Evaporator Coils
An evaporator coil is a key component in an air conditioning system or heat pump system as they absorb heat from indoor air. As warm air passes over the coil, refrigerant inside the coil evaporates, pulling heat from the air and cooling it. The cooled air is then circulated back into the space, while the refrigerant, now a gas, moves to the outdoor unit to release the absorbed heat.
Boilers
A boiler is a heating system that heats water or produces steam to warm a home. It works by burning fuel (such as natural gas, oil, or electricity) to heat water, which is then circulated through pipes to radiators, baseboards, or underfloor systems, or it generates steam for heating. The heat is then transferred to the air in the space, providing consistent warmth throughout the building.
Indoor Air Quality Products
A plethora of indoor air quality products can be added to your HVAC system to help manage humidity and ventilation, helping you breathe cleaner air.
- Air purifiers trap and reduce contaminants like pollen, dust, dander, select airborne viruses, and bacteria to keep your indoor air cleaner.
- Humidifiers and dehumidifiers work to control the humidity of your home.
- Ventilators bring fresh outdoor air into your home while removing stale air from your home.
- UV lamps can kill mold and bacteria on your cooling coil.
- Check out Carrier’s full line of indoor air quality solutions.

Choosing The Right HVAC System
Selecting the right HVAC system for your home involves considering several critical factors. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your specific needs. Here are some essential points to consider:
Size of Your Home
The size of your home significantly influences the capacity of the HVAC system you need. Ensuring that your HVAC system is appropriately sized for your home is crucial. Oversized systems can lead to inefficient operation, while undersized systems may struggle to maintain desired comfort levels. A professional contractor can perform a load calculation to determine the appropriate size for your home.
Climate
The climate in your area also impacts your HVAC equipment choice. If you live in a region with extreme temperatures, you may need a system with higher heating or cooling capabilities.
Energy Efficiency Ratings and Certifications
When shopping for HVAC systems, pay attention to energy efficiency ratings and certifications. Energy-efficient HVAC systems can lower your utility bills and positively impact the environment. Look for HVAC equipment with ENERGY STAR® certification, which meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Additionally, check the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER2) rating for air conditioners and the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating for furnaces.
Connect With A Carrier Dealer On An HVAC Unit For Your Home
At Carrier, we recognize the critical role that HVAC systems play in your home. Our range of high-quality HVAC equipment is designed to offer optimal comfort, energy efficiency, and reliability for your home. Connect with your local Carrier dealer to find the right heating and cooling solution for your home. Our HVAC system builder can provide you with a HVAC system recommendation for your home based on your heating and cooling needs and preferences.
Browse Carrier HVAC Systems
Browse Carrier HVAC systems for reliable, energy-efficient heating and cooling solutions that offer comfort, performance, and long-term value. With advanced technology, quiet operation, and a wide range of models, Carrier systems are designed to meet the unique needs of your home. Whether you're looking for energy savings, improved air quality, or smarter temperature control, Carrier's innovative HVAC solutions ensure year-round comfort.
Frequently Asked Questions
Learn More About Heating and Air Conditioning Units
- Learn about different HVAC system types
- Discover the ins and outs of HVAC repair service
- Understand the importance of HVAC maintenance
- Learn the ins and outs of HVAC installation and AC installation
- Discover HVAC replacement cost
- Learn what is a heat pump and how a heat pump works
- Get information about the cost of a heat pump
- Learn about air conditioner prices
- Discover how an air conditioner works
- What to consider when buying a furnace
- Read our guide to gas furnaces
- Have hot or cold spots in your home? Consider installing a ductless mini split
- HVAC meaning: What is HVAC?
- What is a two-stage HVAC system?
- Discover HVAC options for old houses











