Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV) System Guide
By Travis Baugh
In this article, we'll delve into the world of heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) and explore how a heat recovery ventilation system can significantly enhance indoor air quality and energy efficiency in your home.
What is a Heat Recovery Ventilator (HRV)?
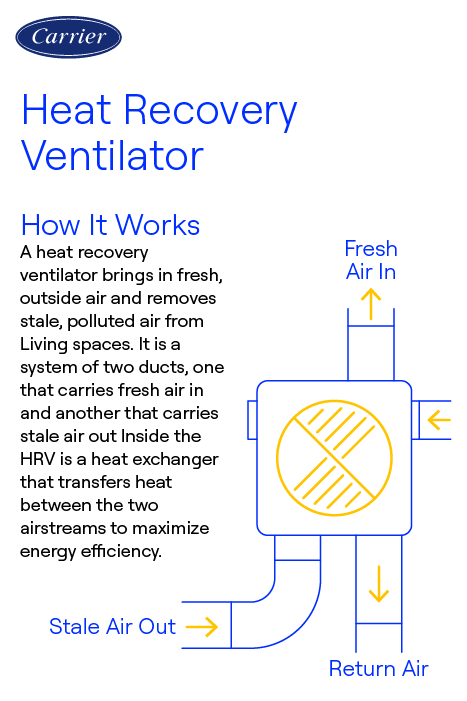
A heat recovery ventilator, also known as an HRV, is a crucial component of a well-designed HVAC system. It is a mechanical ventilation system that ensures a healthier indoor environment by exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air.
The primary function of a heat recovery ventilator is to recover heat from the exhaust air and transfer it to the incoming fresh air, thus boosting energy efficiency while maintaining proper ventilation. This is especially advantageous during colder months when opening windows for ventilation leads to significant heat loss.
What is the Difference Between a HRV and ERV?
HRVs (Heat Recovery Ventilators) and ERVs (Energy Recovery Ventilators) are both mechanical ventilation systems designed to improve indoor air quality by exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air. The main difference lies in how they manage moist air. Unlike an energy recovery ventilator system (ERV), which also transfers moisture content between air streams, a heat ventilation recovery system focuses mainly on heat exchange. This makes heat recovery ventilation systems particularly beneficial in climates where humidity control is less of a concern, such as northern climates An ERV, on the other hand, transfers both heat and moisture, helping to retain indoor humidity in winter and reduce excess humidity in summer—making energy recovery ventilation systems a better fit for more humid or variable climates.
While neither system is strictly “better,” one may be more suitable based on your regional climate, indoor humidity needs, and home design. Both systems are typically installed with ductwork, so existing HVAC layout and space availability should be considered. For homes without ductwork or with limited space, consult your local Carrier dealer to determine the best ventilation solution.
“A heat recovery ventilator, or HRV, provides many of the same benefits as an ERV in that it brings fresh outdoor air into the home while exhausting stale indoor air,” Kevin Dickson, president of Energy Services Air Conditioning, Heating and Electrical in Naperville, Illinois, said. “The key difference is that an HRV is designed to transfer heat from the outgoing air to the incoming air, which makes it especially valuable in colder climates. By pre-warming the incoming air, an HRV reduces the burden on your heating system, helps maintain consistent indoor temperatures, and prevents drafts from cold outside air. For homeowners, this means better indoor air quality, improved comfort during the winter months, and increased energy efficiency. Families who deal with tightly sealed homes in cold regions can especially benefit from an HRV because it balances the need for ventilation with the need to stay warm and control energy costs.”

What are the benefits of a heat recovery ventilator?
Using a heat recovery ventilator in your home offers numerous benefits
- They remove pollutants such as allergens, dust, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) while supplying fresh outdoor air. This is particularly vital in tightly sealed homes that lack sufficient natural ventilation.
- Heat recovery ventilation systems help maintain comfortable indoor temperatures by recovering heat from the exhaust air, reducing the reliance on heating systems, which may help reduce heating and cooling bills.
- HRV systems provide balanced ventilation. Balanced ventilation ensures an even exchange of indoor and outdoor air, which is crucial to help maintain neutral pressure in the home unlike an exhaust only fan that could create negative pressure.
- By improving energy efficiency and reducing the need for additional heating or cooling, HRVs reduce a home’s carbon footprint.
How Do Heat Recovery Ventilators Work?
An heat recovery ventilator is a mechanical ventilation system that maintains a healthier indoor environment by exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air. It utilizes a sophisticated mechanism to recover heat from the outgoing stale air to pre-condition the incoming fresh air, thereby improving energy efficiency. Learn more about what is home ventilation.
The functioning of an HRV system is based on the principle of heat transfer. The unit consists of two separate air streams: one for the outgoing stale air and another for the incoming fresh air. These air streams pass through a heat recovery core made of a membrane that allows the transfer of heat between the air streams.
As the stale indoor air is expelled, it transfers its heat to the heat exchanger. Simultaneously, the fresh outdoor air passes through the opposite side of the heat exchanger, where it is preheated or precooled by the outgoing air, depending on the season.
Integrating a heat recovery ventilation system with an existing HVAC system can enhance indoor air quality and energy efficiency. Using existing ductwork, the heat recovery ventilator can exchange stale, polluted air with fresh outdoor air while recovering heat from outgoing air to pre-condition incoming air.
Proper placement of the heat recovery ventilator is essential for optimal performance, ensuring balanced air exchange throughout the home. Regular cleaning and filter replacement are necessary to maintain the system's efficiency and prevent dust and pollutant buildup.

The Importance of Indoor Air Quality
Indoor air quality (IAQ) plays a vital role in overall health and comfort. Poor IAQ can potentially lead to respiratory issues, allergies, and fatigue due to pollutants like dust, mold, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Maintaining good indoor air quality helps ensure a healthier living environment.
Proper ventilation is key to maintaining indoor air quality. It helps remove stale air, control humidity, and prevent the buildup of indoor pollutants. Without adequate ventilation, contaminants accumulate, leading to poor air circulation and discomfort.
A heat recovery ventilator (HRV) is an excellent solution for improving IAQ. HRVs exchange stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air while recovering heat energy, making them energy-efficient. This not only improves air quality but also reduces heating and cooling costs. By incorporating HRVs into home ventilation systems, homeowners can enjoy fresh, clean air year-round, ensuring a comfortable and healthier indoor environment.
Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems and Energy Efficiency
Heat recovery ventilators are an excellent way to improve energy efficiency in homes. Heat recovery ventilation systems recover and reuse heat that would otherwise be lost during ventilation, helping to reduce energy waste and lower heating and cooling bills.
By extracting heat from outgoing stale air and transferring it to incoming fresh air, heat recovery ventilation systems ensure that the energy used to heat or cool indoor air is not wasted. This process leads to significant energy savings, as conditioned air retains much of its temperature when reintroduced into the living space.
One of the key benefits of heat recovery ventilation systems is their ability to reduce heating and cooling costs. By recovering heat from exhaust air, heat recovery ventilation systems decrease the energy required to heat incoming fresh air during winter. Similarly, during summer, the system helps pre-cool incoming air, reducing reliance on air conditioning. This results in lower energy consumption and substantial savings on heating and cooling bills.

Heat Recovery Ventilator Installation
- Home Assessment: The dealer inspects your home layout, HVAC system, and ventilation needs.
- System Selection: Based on your assessment, they recommend the right Carrier HRV model.
- Installation: The dealer professionally installs the HRV, including ductwork, vents, and controls.
- Testing & Commissioning: The system is tested for airflow, temperature recovery, and proper operation.
- Education: Homeowners are guided on operating controls and maintenance schedules.
Heat Recovery Ventilator (HRV) Maintenance
Key Maintenance Tasks
- Clean or Replace Filters – HRV filters capture dust, pollen, and debris. Clean them every 1-3 months and replace them as needed to maintain efficient airflow.
- Inspect and Clean the Core – The heat exchange core should be cleaned every 6-12 months with warm water or a vacuum to remove accumulated dirt.
- Check and Clean Vents & Ducts – Ensure that both indoor and outdoor vents are free from blockages like leaves, dust, or ice buildup. Clean ductwork periodically to maintain proper air circulation.
- Inspect the Drainage System – If your HRV has a condensate drain, check for clogs and clean it to prevent water buildup.
- Test the Fans and Motors – Ensure fans run smoothly and listen for unusual noises that may indicate wear or damage.
Choosing The Right HRV Systems for Homes
At Carrier, we understand the importance of proper ventilation in your home. Our range of ventilation systems are designed to provide improved indoor air quality while maximizing energy savings. Incorporating advanced technology and key features, our heat recovery ventilators offer a reliable and efficient solution for your ventilation needs.
Choosing the right heat recovery ventilation system is crucial for ensuring a healthier and comfortable indoor environment. Connect with your local Carrier dealer to find the right heat recovery ventilator for your home. Working with your Carrier dealer on a heat recovery ventilator (HRV) ensures you get expert guidance on selecting, installing, and maintaining the right system for your home. Carrier dealers are trained on HRV installation and to optimize HRV performance for maximum energy efficiency, air quality, and comfort. Plus, they provide professional service, warranty support, and routine maintenance to keep your system running smoothly for years to come. Schedule an appointment with your local Carrier dealer today.

Frequently Asked Questions About Heat Recovery Ventilators
Explore Carrier HRV HVAC Systems
A Carrier heat recovery ventilator (HRV) enhances indoor air quality by efficiently exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air, while retaining energy. It helps maintain optimal humidity and temperature levels throughout the year, promoting a healthier and more comfortable living environment. By reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling, an HRV also contributes to energy savings, making it an eco-friendly choice for homeowners. Explore Carrier's line of heat recovery ventilators today.
Ideal for northern climates and horizontal installations. Offers airflow up to 231 cubic feet per minute. Door color is slowly transitioning from tan to galvanized steel.*
Ideal for northern climates and horizontal installations. Offers airflow up to up to 160 cubic feet per minute.
Ideal for northern climates and vertical installations. Offers airflow up to 160 cubic feet per minute




